Teano, Monastery of Sant'Antonio da Padova
2021
On the top of the homonymous hill stands the Franciscan monastic complex dedicated to St. Anthony of Padua, a true symbol of Sidycin and non-Sidycin Christian devotion. Much has been written about the monastic complex in recent decades and almost everything is known about it by now. The monastery was built in 1427 by the Franciscan friars Martino di Campagna and Nicola di Castellammare di Stabia on a land owned by the knight Ludovico Galluccio
You may also like
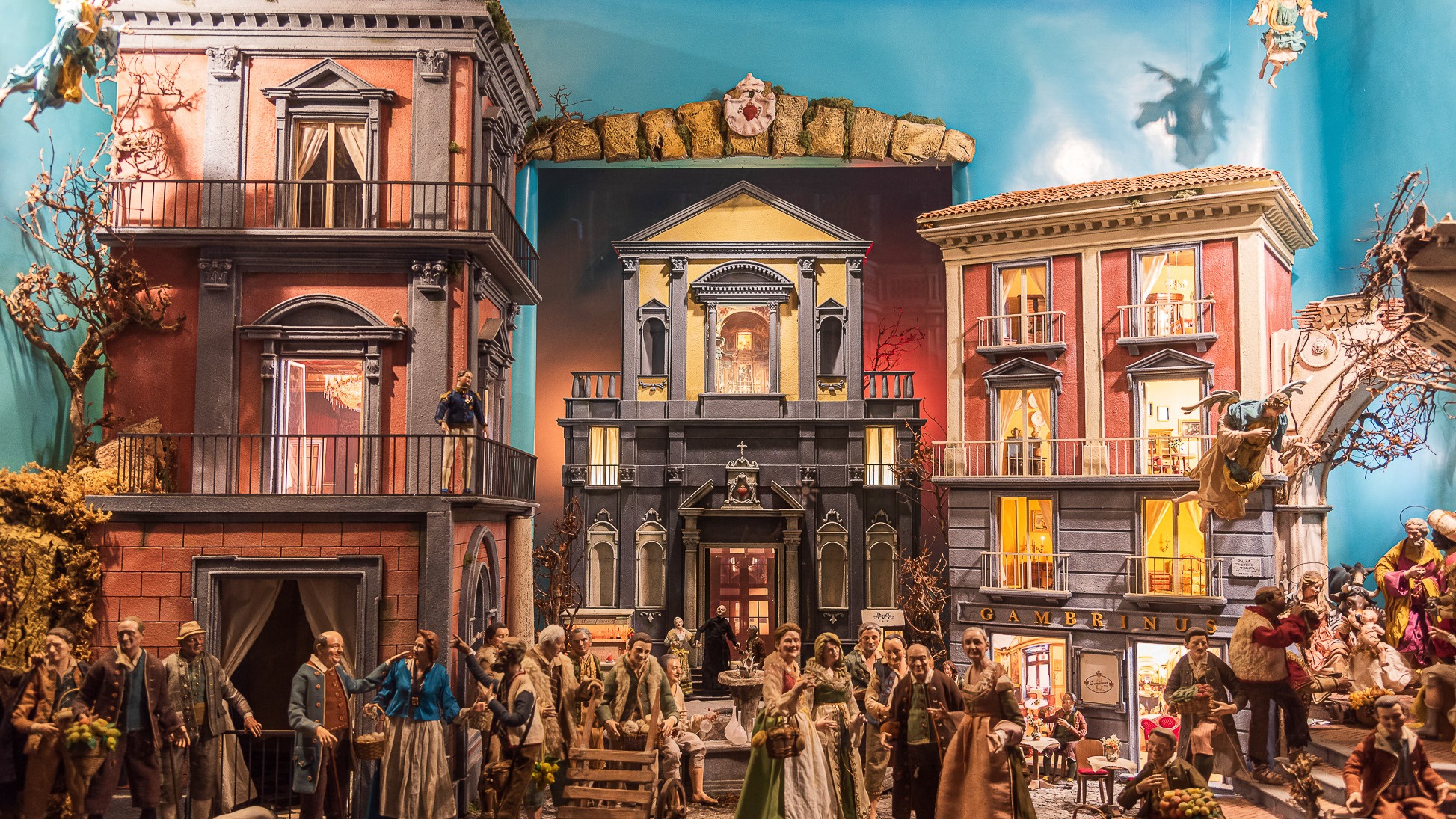

2023
Naples. The church of San Ferdinando
The church of San Ferdinando is a monumental church in Naples located in the historic center of the city, in Piazza Trieste e Trento.
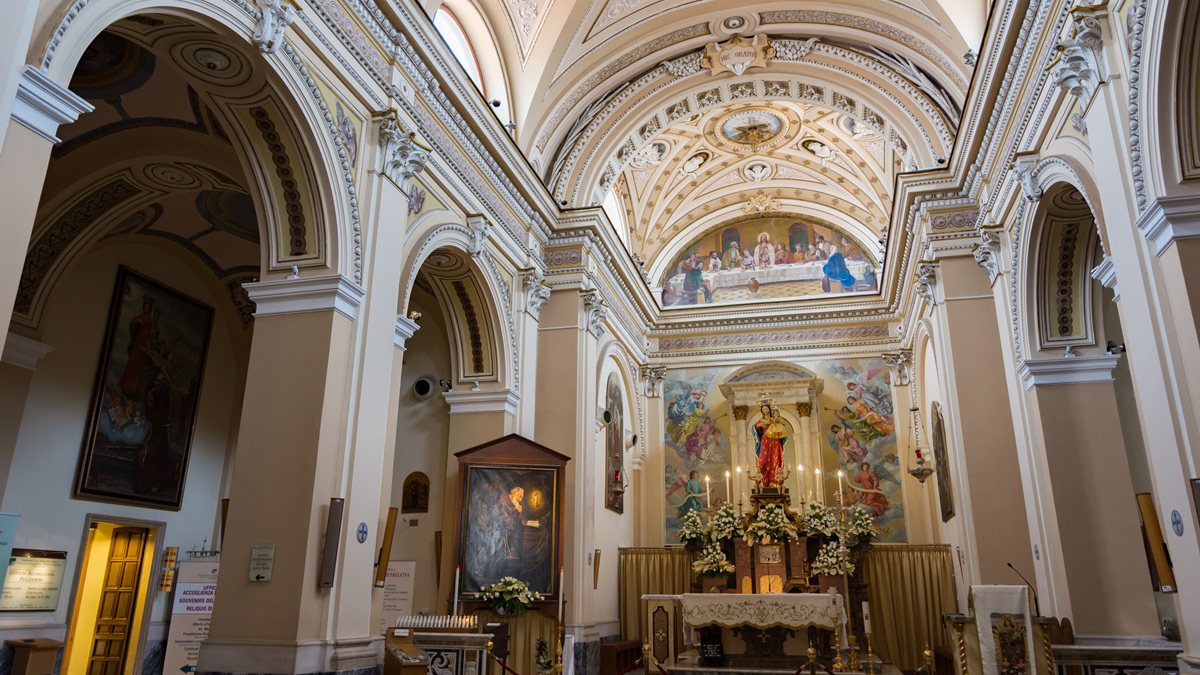

2017
Pietrelcina (BN), church of Santa Maria degli Angeli
Santa Maria degli Angeli, parish church of Pietrelcina, preserves the polychrome wooden statue of the Neapolitan school of the end of the seventeenth century depicting the Madonna della Libera, patron saint of Pietrelcina, which Padre Pio affectionately calls "our Madonnella". In this church Fra Pio began his apostolate and, having obtained the diaconate, he administered the first baptism to a child who later became a Redemptorist priest. In this regard it is said that Padre Pio put so much salt, that the newborn, opening his little mouth, squinted his eyes - "smerzava l`uocchie" - words of Brother Pio, who frightened ran to the archpriest Don Salvatore Pannullo, saying: " I killed the child ”. On the eve of the solemnity of the Assumption, on 14 August 1910, four days after being ordained a priest, Padre Pio celebrated his first mass. A few days later he wrote to Father Benedetto of San Marco in Lamis: "For several days I was a little sick; perhaps the main cause of this was the too much emotion to which the spirit has been subject in these days… my heart is overflowing with joy and it feels stronger and stronger to encounter any affliction, when it comes to pleasing Jesus ”. In this church Padre Pio had interminable moments of prayer and intimacy with God, ecstasy at the foot of the altar, and the mystical phenomenon of the fusion of hearts: "The heart of Jesus and mine, allow me the expression, were no longer two hearts that beat, but only one. My heart was gone, like a drop of water that gets lost in the sea ”. And again: "I feel everything burn without fire ... a thousand flames consume me, I feel I am dying continuously and still alive". Padre Pio celebrated masses in this church that were "too long" and "incomprehensible mystery" so much so that the guardian father had asked the parish priest to recall him in his mind, because in this way he would immediately obey him out of holy obedience.
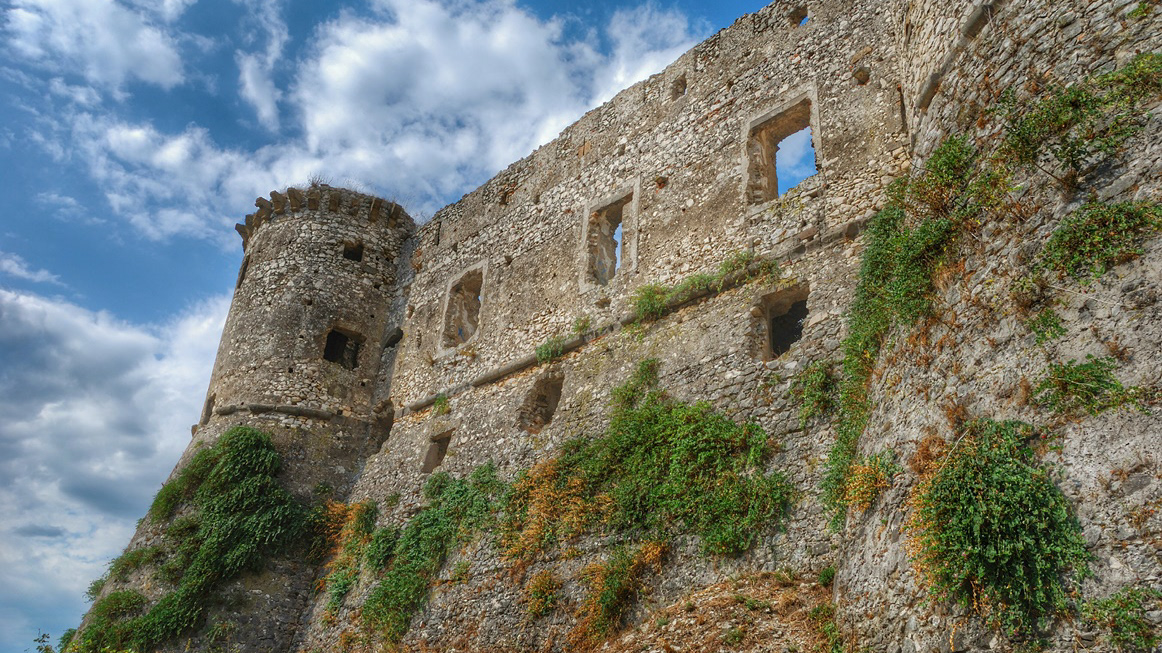

2007
Vairano Patenora (CE), the Aragonese Castle
The Aragonese castle of Vairano was built on the remains of the Norman and Swabian ones between 1491 and 1503 by Innico II d'Avalos. It has four towers of which the largest, located to the south-east, is called "Torre mastra" and has an open atrium entrance. The interior is destroyed, but the subdivision of the floors, the kitchens, the prisons and the old cistern are still visible.

2021
Teano. Church of San Michele Arcangelo

2020
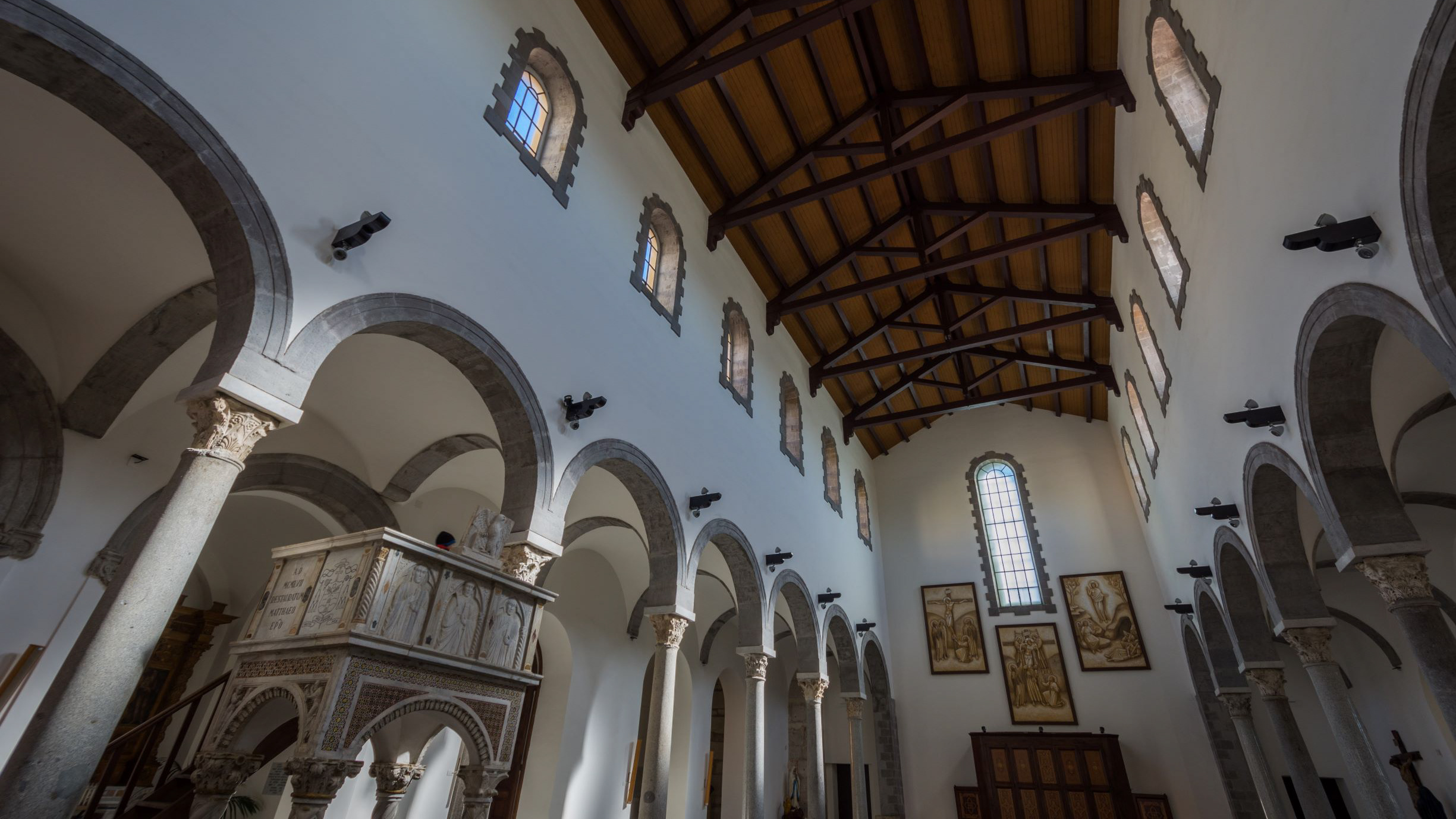
Teano. The Cathedral. The central nave
The cathedral, originally dedicated to San Terenziano, was later named after San Clemente. Construction began in 1050 by Bishop Guglielmo, to replace the old cathedral of San Paride ad Fontem, located outside the city walls. The works were completed in 1116 by Bishop Pandulfo. The building has a basilica structure divided into three naves by two rows of columns. In 1608 it was damaged internally by a fire that almost completely destroyed the cosmates ambo, subsequently recomposed using the remains of the previous one integrated with the marble slabs of a fourteenth-century sepulchral monument already present in the church and positioned on twisted columns, two of which rested on fountain lions. During the 16th century the Romanesque apse was modified and on that occasion a precious carved wooden choir was built in the presbytery, built in 1539 by the Benedictine Antonio Maria Sertorio. The choir underwent two restorations, the first in the 17th century and the second in 1957, following the damage suffered during the Second World War.

2021
Teano, Frazione Furnolo
2023
Teano. Church of San Francesco.
Teano. Church of San Francesco. Built in the fourteenth century, in Gothic style, by the Conventual Minors it was extensively remodeled in the Baroque age.

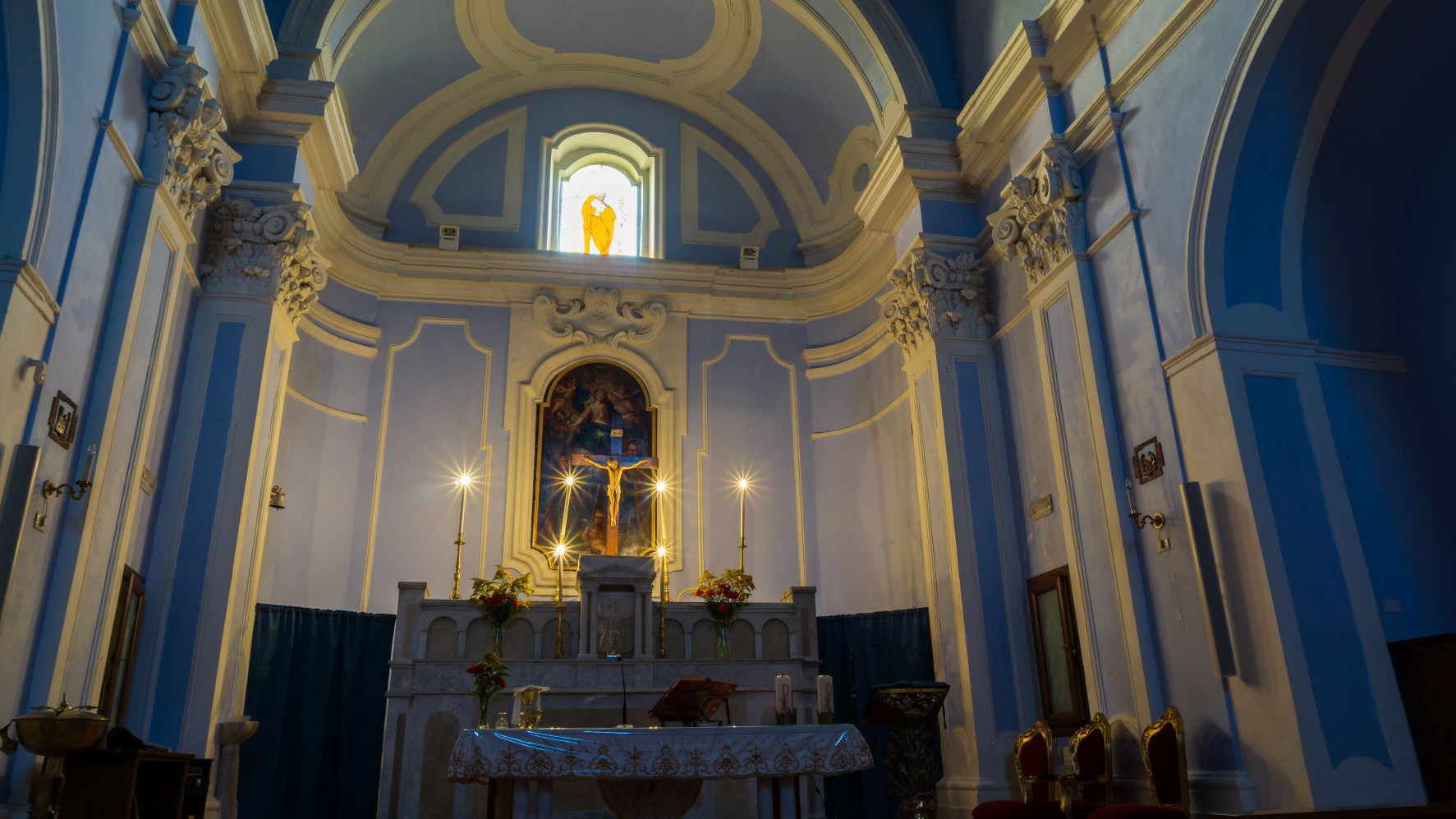
2020
Teano. The Cathedral. Left side chapel
The cathedral, originally dedicated to San Terenziano, was later named after San Clemente. Construction began in 1050 by Bishop Guglielmo, to replace the old cathedral of San Paride ad Fontem, located outside the city walls. The works were completed in 1116 by Bishop Pandulfo. The building has a basilica structure divided into three naves by two rows of columns. In 1608 it was damaged internally by a fire that almost completely destroyed the cosmates ambo, subsequently recomposed using the remains of the previous one integrated with the marble slabs of a fourteenth-century sepulchral monument already present in the church and positioned on twisted columns, two of which rested on fountain lions. During the 16th century the Romanesque apse was modified and on that occasion a precious carved wooden choir was built in the presbytery, built in 1539 by the Benedictine Antonio Maria Sertorio. The choir underwent two restorations, the first in the 17th century and the second in 1957, following the damage suffered during the Second World War.
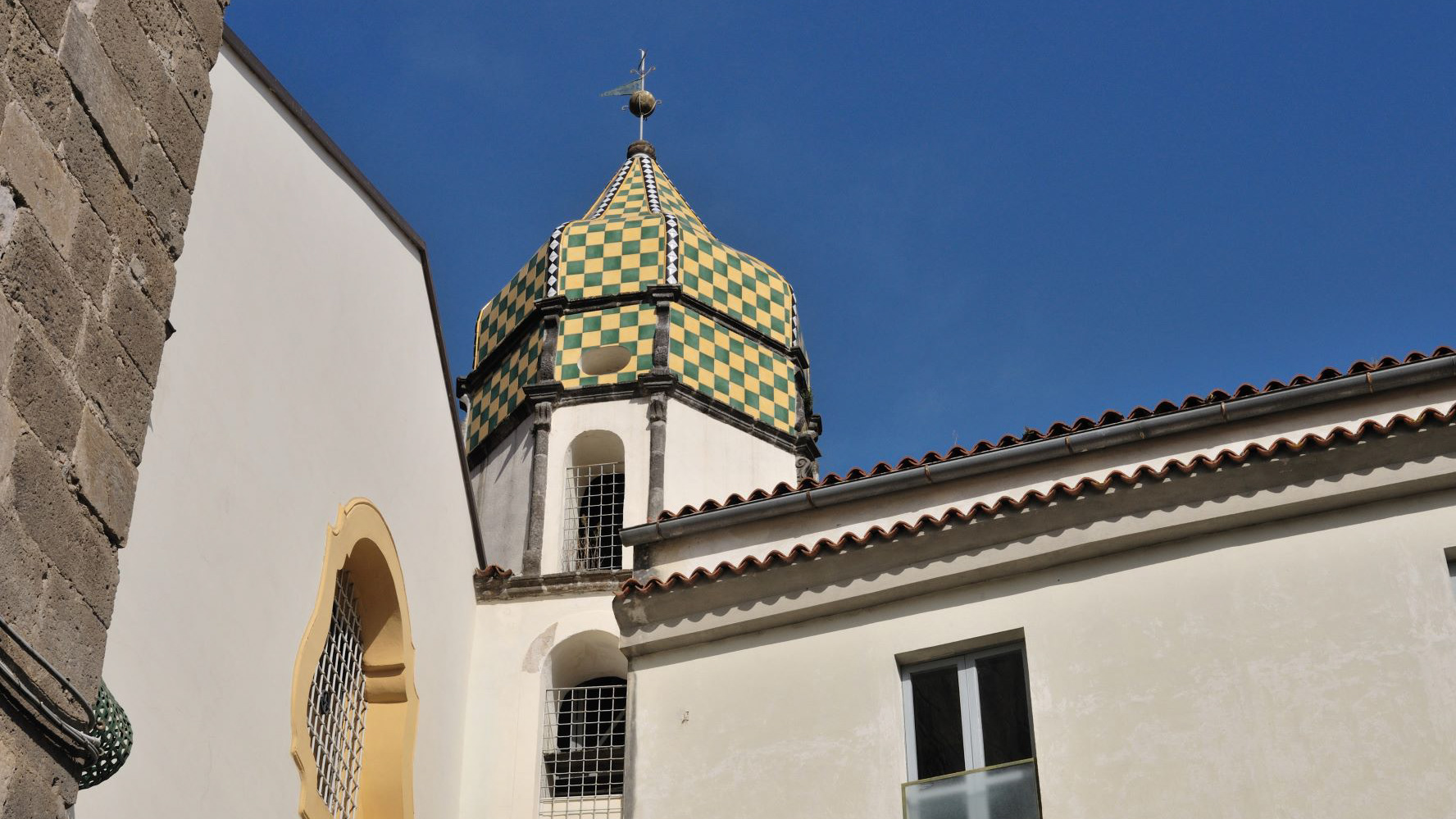

2021
Teano. Monastery of Santa Caterina
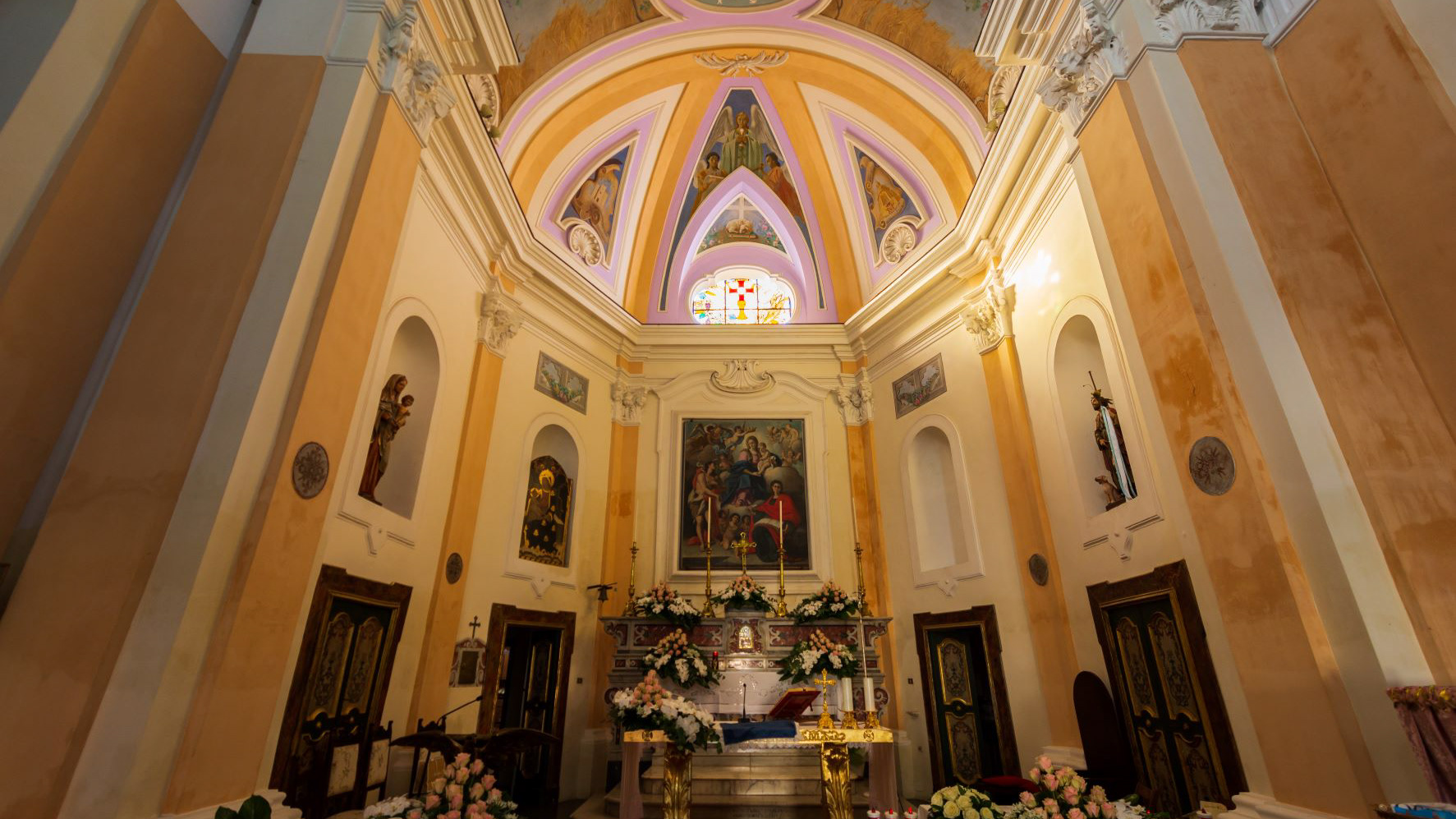
2021
Francolise, Santa Maria a Castello
