Campania Felix
2018
Ancient Campania (often also identified as Campania Felix or even Ager Campanus) originally indicated the territory of the city of Capua Antica in the Roman period, and later also the plains of the various neighboring municipalities. It was a very vast territory when compared with the other Italic cities of the Roman and pre-Roman periods. It stretched from the slopes of Mount Massico (in the north) to the south of the Phlegrean Fields and the Vesuvian area. Initially it also included the ager Falernus, then it was greatly scaled down from Rome due to the alliance of the city of Capua with Annibale. Thanks to the fertility of the soil also due to the presence of the Volturno river, it deserved the name of Campania Felix.
You may also like

2021
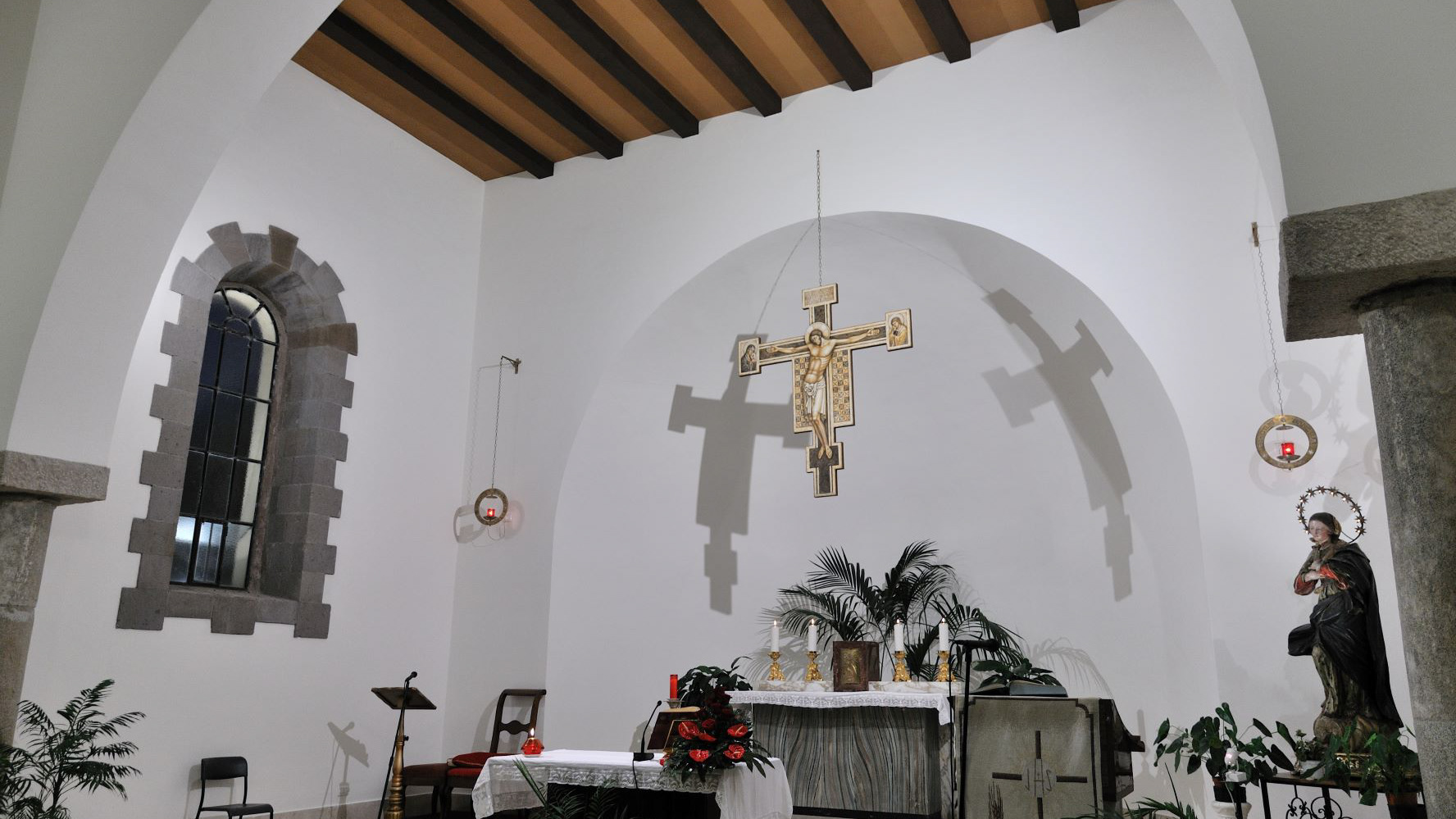
Teano, the Cathedral. Left side chapel
The cathedral, originally dedicated to San Terenziano, was later named after San Clemente. Construction began in 1050 by Bishop Guglielmo, to replace the old cathedral of San Paride ad Fontem, located outside the city walls. The works were completed in 1116 by Bishop Pandulfo. The building has a basilica structure divided into three naves by two rows of columns. In 1608 it was damaged internally by a fire that almost completely destroyed the cosmates ambo, subsequently recomposed using the remains of the previous one integrated with the marble slabs of a fourteenth-century sepulchral monument already present in the church and positioned on twisted columns, two of which rested on fountain lions. During the 16th century the Romanesque apse was modified and on that occasion a precious carved wooden choir was built in the presbytery, built in 1539 by the Benedictine Antonio Maria Sertorio. The choir underwent two restorations, the first in the 17th century and the second in 1957, following the damage suffered during the Second World War.
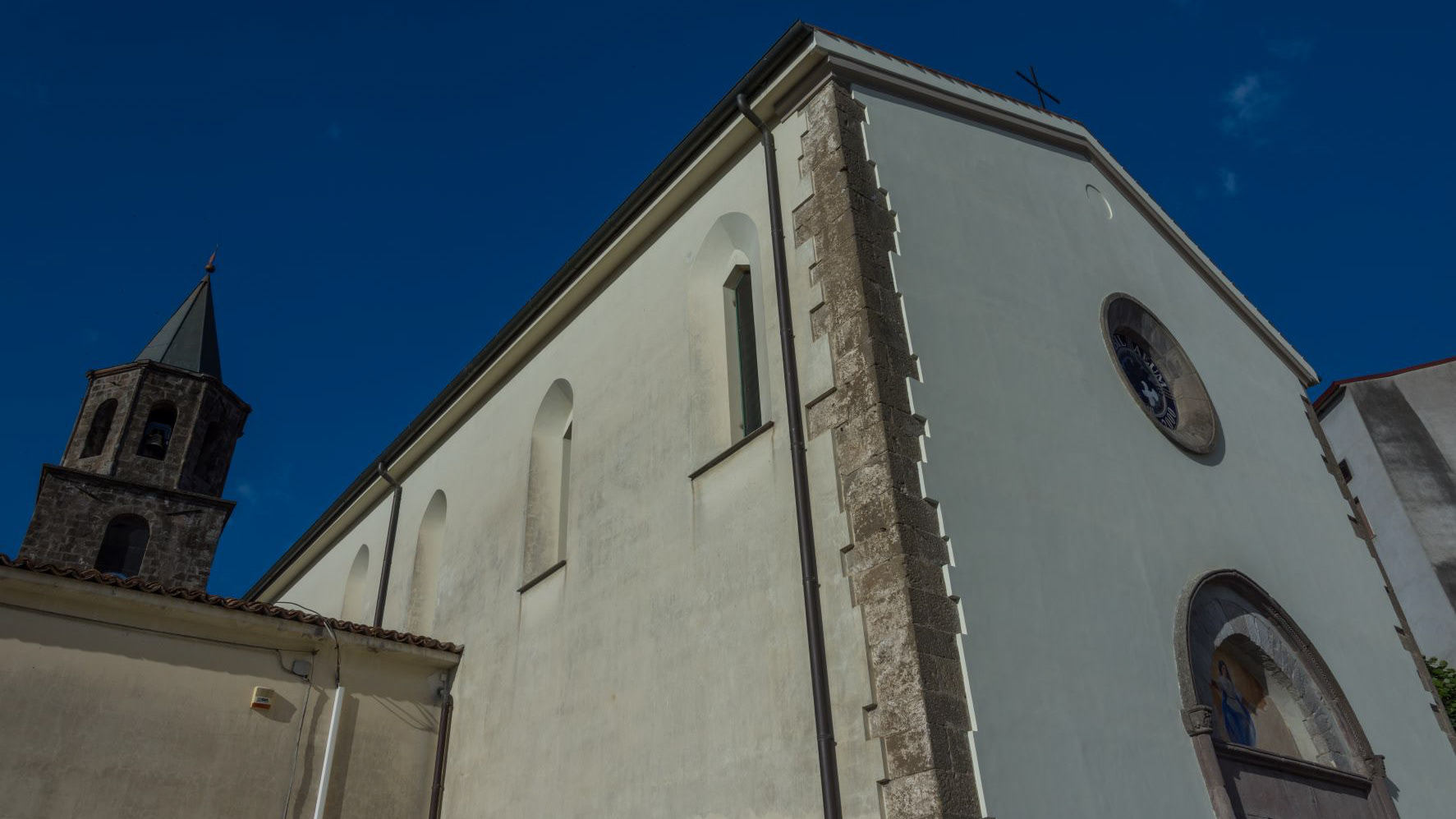

2021
Teano. Church of Santa Maria La Nova

2022
Caserta, the Royal Palace. The park.
The Royal Palace of Caserta is a royal residence, historically belonging to the Bourbons of the Two Sicilies, located in Caserta. Commissioned by Charles of Bourbon, the laying of the first stone, which started the construction work, took place on January 20, 1752, based on a project by Luigi Vanvitelli: this was followed by his son Carlo and other architects. The palace was completed in 1845.
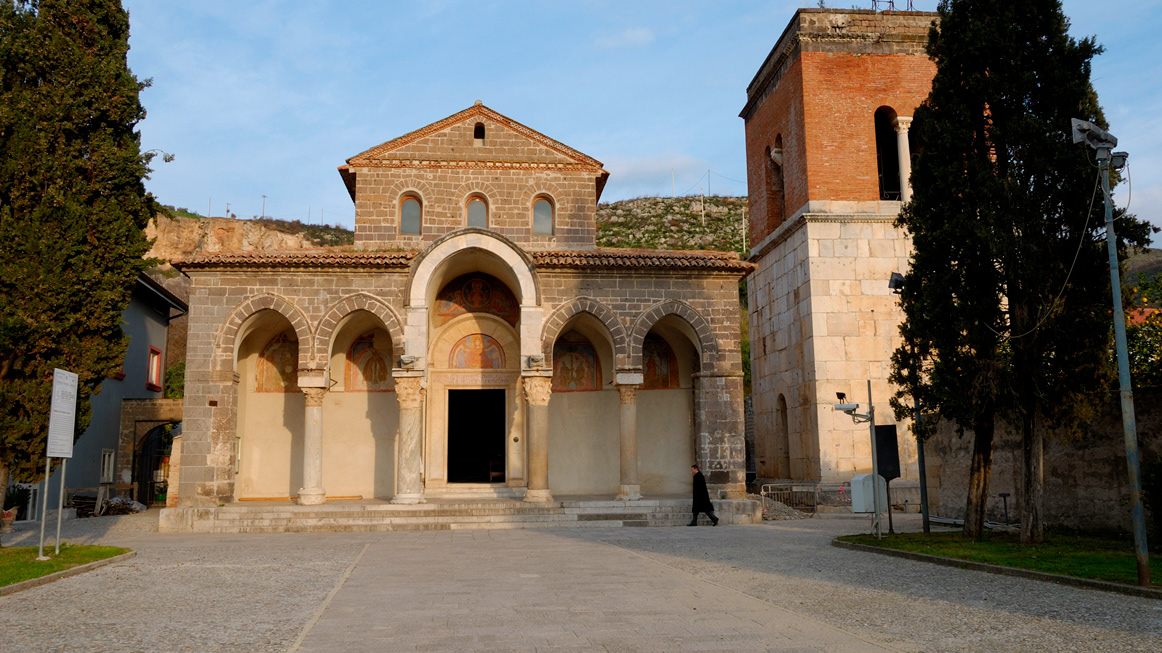

2008
Benedictine Abbey of S. Angelo in Formis
The church, dedicated to San Michele Arcangelo, rises along the western slope of Mount Tifata. Initially in the documents the building is indicated as ad arcum Dianae ("at the arch of Diana"), recalling that it stood above the remains of the temple dedicated to this divinity, while later it is referred to with the denominations ad Formas , Informis or in Formis. The etymological interpretation of the new name is controversial: on the one hand, the hypothesis is that it derives from the Latin term forma ("aqueduct"), and that it indicates the proximity of a conduit or aquifer; while on the other hand the term is considered derived from the word informis ("formless", and therefore "spiritual"). The remains of the Roman temple were found in 1877, and it has been noted that the basilica retraces its perimeter, adding the apses at the end of the aisles. The first construction of the basilica can be traced back to the Lombard period, on the basis of the widespread diffusion of the cult of the archangel Michael among the Lombards at the end of the sixth century. At the time of the bishop of Capua Pietro I (925-938), the church was donated to the monks of Montecassino, who wanted to build a monastery there. The church was then taken from the monks and given back to them in 1072 by the prince of Capua, Riccardo. The then abbot Desiderio di Montecassino (the future Pope Victor III) decided to rebuild the basilica (1072 - 1087) and still respected the architectural elements of pagan origin. To him we owe the frescoes of the Byzantine-Campanian school that decorate the interior and which constitute one of the most important and best preserved pictorial cycles of the time in southern Italy. The reconstruction of the portico in front of the church, with new frescoes, and a reconstruction of the bell tower following a collapse have been attributed to the 12th century
2022
Teano, the Cathedral of San Clemente.
The cathedral of San Clemente is the main place of worship in the city of Teano, in Campania, and the seat of the diocese of Teano-Calvi

2017
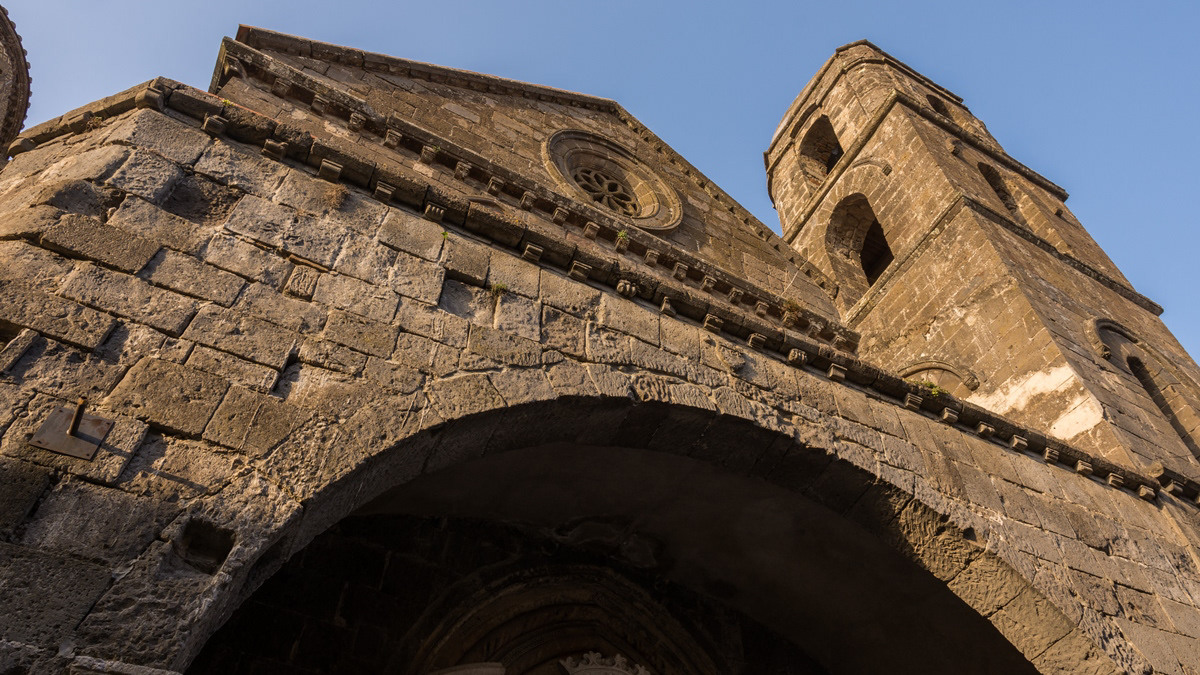
Casertavecchia, church of the Annunciation

2021
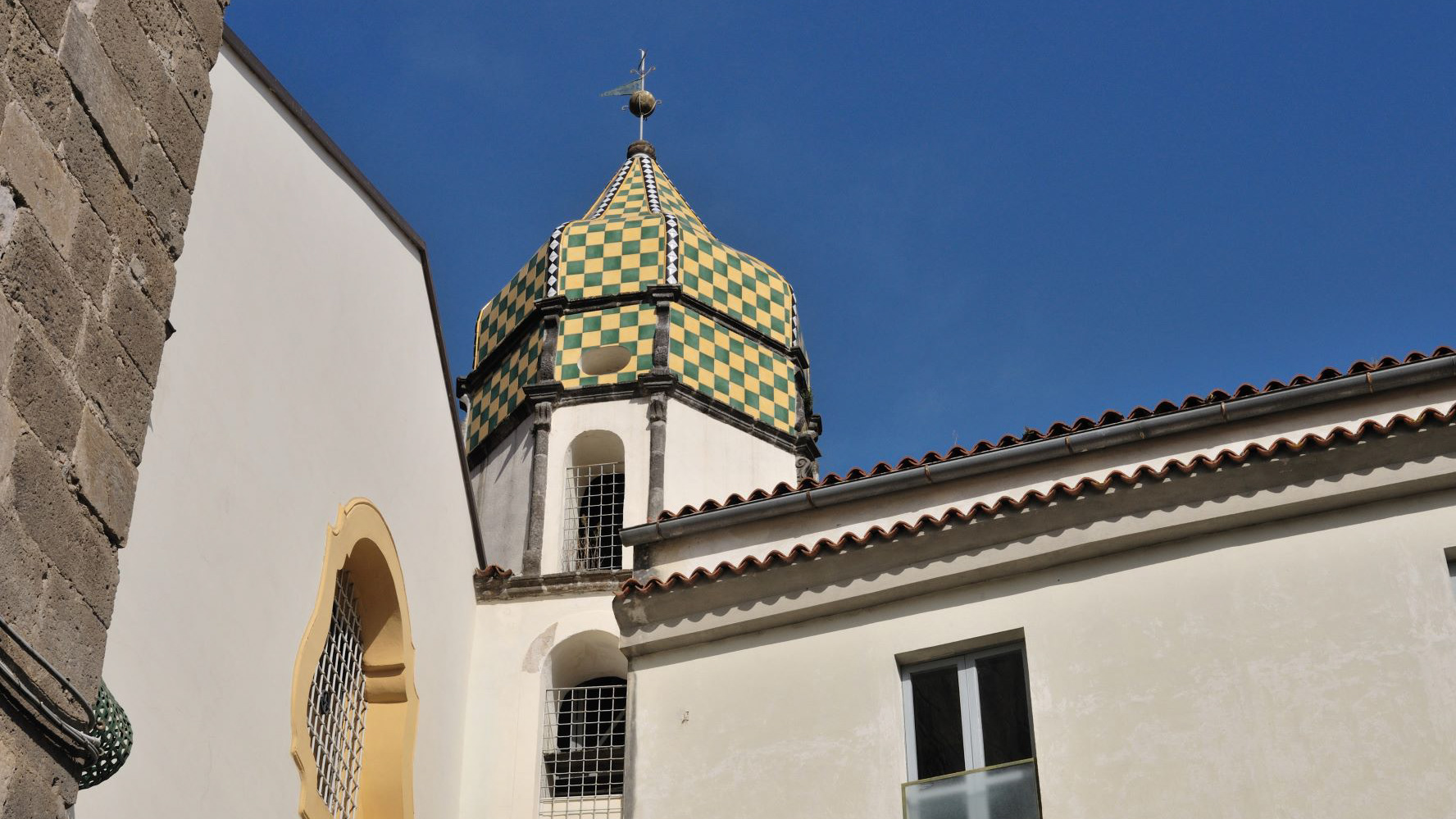
Teano. Monastery of Santa Caterina
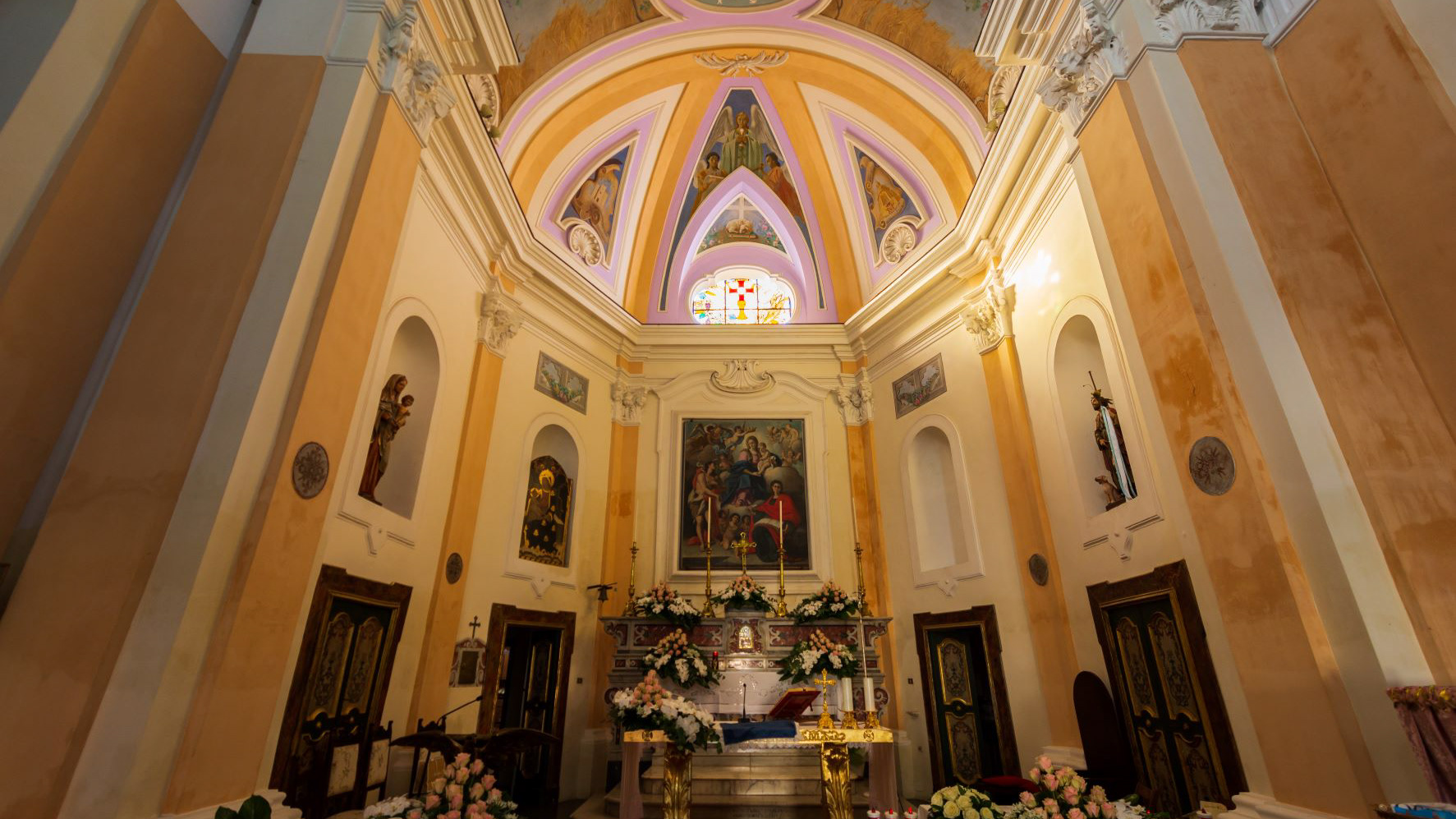
2021
Francolise, Santa Maria a Castello

2017
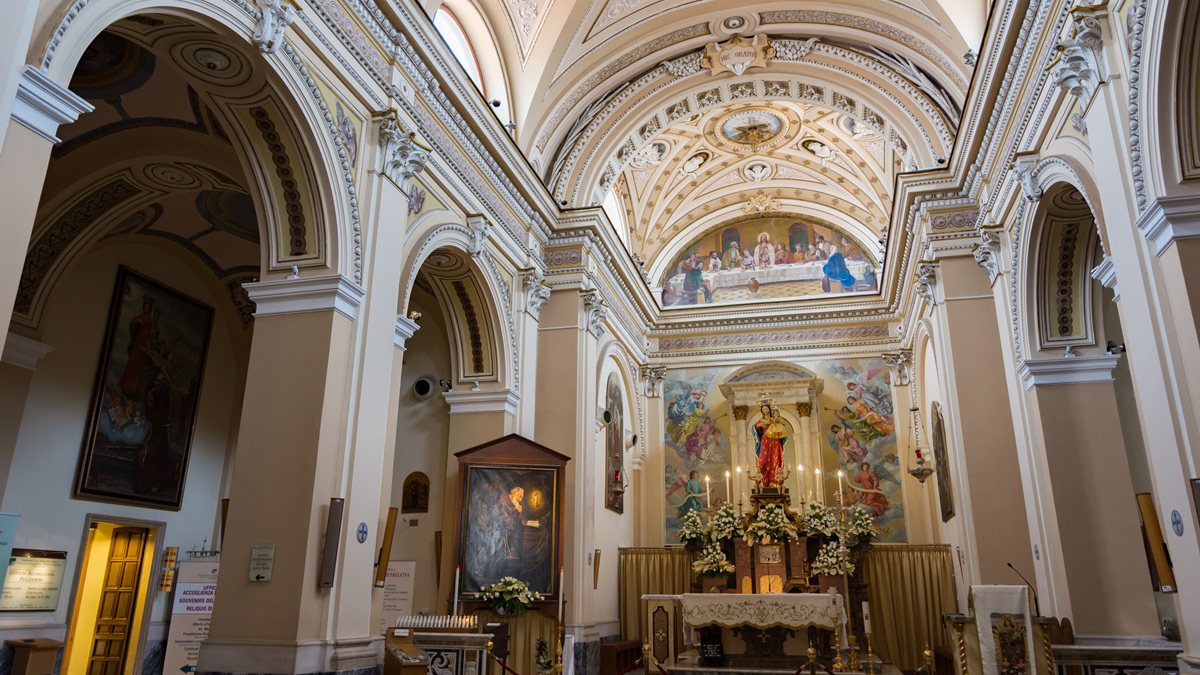
Pietrelcina (BN), church of Santa Maria degli Angeli
Santa Maria degli Angeli, parish church of Pietrelcina, preserves the polychrome wooden statue of the Neapolitan school of the end of the seventeenth century depicting the Madonna della Libera, patron saint of Pietrelcina, which Padre Pio affectionately calls "our Madonnella". In this church Fra Pio began his apostolate and, having obtained the diaconate, he administered the first baptism to a child who later became a Redemptorist priest. In this regard it is said that Padre Pio put so much salt, that the newborn, opening his little mouth, squinted his eyes - "smerzava l`uocchie" - words of Brother Pio, who frightened ran to the archpriest Don Salvatore Pannullo, saying: " I killed the child ”. On the eve of the solemnity of the Assumption, on 14 August 1910, four days after being ordained a priest, Padre Pio celebrated his first mass. A few days later he wrote to Father Benedetto of San Marco in Lamis: "For several days I was a little sick; perhaps the main cause of this was the too much emotion to which the spirit has been subject in these days… my heart is overflowing with joy and it feels stronger and stronger to encounter any affliction, when it comes to pleasing Jesus ”. In this church Padre Pio had interminable moments of prayer and intimacy with God, ecstasy at the foot of the altar, and the mystical phenomenon of the fusion of hearts: "The heart of Jesus and mine, allow me the expression, were no longer two hearts that beat, but only one. My heart was gone, like a drop of water that gets lost in the sea ”. And again: "I feel everything burn without fire ... a thousand flames consume me, I feel I am dying continuously and still alive". Padre Pio celebrated masses in this church that were "too long" and "incomprehensible mystery" so much so that the guardian father had asked the parish priest to recall him in his mind, because in this way he would immediately obey him out of holy obedience.

2021
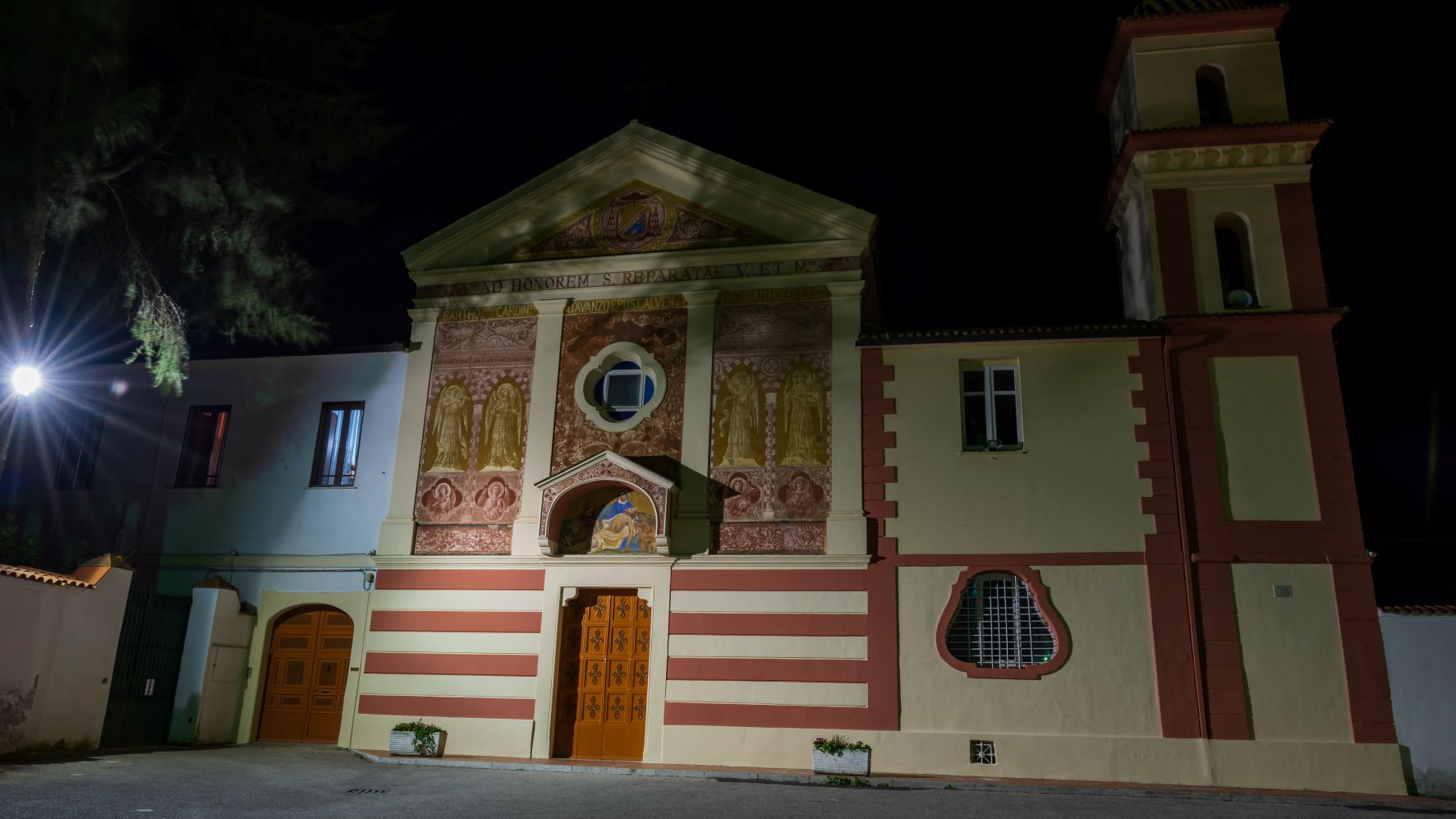
Teano. Church of Santa Reparata
